



Next: B3. Two Norm
Up: B. Optimization
Previous: B1. Jacobian Matrix
B2. Hessian Matrix
The Hessian matrix
 of a scalar function
of a scalar function
 (
(
 )
is defined by the n x n
matrix built out of the second partial derivatives
)
is defined by the n x n
matrix built out of the second partial derivatives
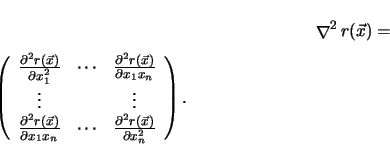 |
(B3) |
The Hessian matrix of the scalar function  is the Jacobian
matrix of the gradient
is the Jacobian
matrix of the gradient
 .
.
R. Plasun
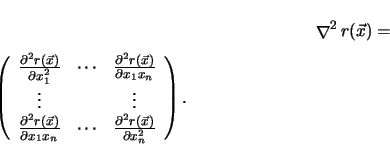
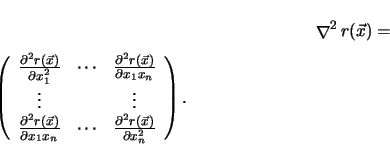
![]() is the Jacobian
matrix of the gradient
is the Jacobian
matrix of the gradient
![]() .
.