



Next: 2.3.3.13 Power Monitor
Up: 2.3.3 Devices
Previous: 2.3.3.11 Current Controlled Voltage
2.3.3.12 Gyrator
The constitutive relations for a linear gyrator are given as
| Iout |
= |
g . Vin, |
(2.42) |
| Iin |
= |
g . Vout |
(2.43) |
where g is the gyrator constant. The gyrator can be modeled with the
classic NA as it is purely voltage controlled. The voltages and currents
are shown in Fig. 2.7 and the stamp is given as
Figure 2.7:
Voltages and currents for a gyrator
![\begin{figure}
\begin{center}
\resizebox{7.8cm}{!}{
\psfrag{IA}{$\scriptstyle I_...
...
\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,angle=0]{figures/gyr.eps}}\end{center}\end{figure}](img126.gif) |
| yx, y |
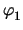 |
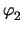 |
 |
 |
r |
| n1 |
|
|
g |
- g |
- Iin |
| n2 |
|
|
- g |
g |
Iin |
| n3 |
- g |
g |
|
|
Iout |
| n4 |
g |
- g |
|
|
- Iout |




Next: 2.3.3.13 Power Monitor
Up: 2.3.3 Devices
Previous: 2.3.3.11 Current Controlled Voltage
Tibor Grasser
1999-05-31
![\begin{figure}
\begin{center}
\resizebox{7.8cm}{!}{
\psfrag{IA}{$\scriptstyle I_...
...
\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,angle=0]{figures/gyr.eps}}\end{center}\end{figure}](img126.gif)