



Next: 6.3.2 CML Inverter
Up: 6.3 Examples
Previous: 6.3 Examples
A simplified schematic of the  A709 operational amplifier output stage is shown in
Fig. 6.8. Transistor T3 acts as a common-emitter
driver stage for the complementary output devices T1 and T2.
Problems are caused by the large bias voltages of
A709 operational amplifier output stage is shown in
Fig. 6.8. Transistor T3 acts as a common-emitter
driver stage for the complementary output devices T1 and T2.
Problems are caused by the large bias voltages of  15 V and by
the sensitivity of the circuit to the state of transistor T3. The
operating point is calculated for
15 V and by
the sensitivity of the circuit to the state of transistor T3. The
operating point is calculated for
 = - 14.5 V
and from this point
= - 14.5 V
and from this point
 is stepped until -14.1I>V. Within this interval the internal state of the circuit changes
completely as
is stepped until -14.1I>V. Within this interval the internal state of the circuit changes
completely as
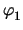 moves from
moves from
 13.6 V down to
13.6 V down to
 - 15 V. With
- 15 V. With
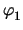 the states of the two output
transistors change.
the states of the two output
transistors change.
Figure 6.8:
Simplified output stage of the  A709 operational amplifier.
A709 operational amplifier.
![\begin{figure}
\begin{center}
\resizebox{7.8cm}{!}{
\psfrag{Vin} {$\scriptstyle ...
...udegraphics[width=7.8cm,angle=0]{figures/gray_5_19.eps}}\end{center}\end{figure}](img498.gif) |
Figure 6.9:
Evolution of the node voltages during DC operating point calculation for the OpAmp output stage with  = 4.
= 4.
![\begin{figure}
\begin{center}
\resizebox{11.4cm}{!}{
\psfrag{5_19_Av.crv:V1} {$\...
...udegraphics[width=11.4cm,angle=0]{figures/5_19conv.eps}}\end{center}\end{figure}](img499.gif) |
Figure 6.10:
Comparison of the iteration counters for a DC transfer characteristic for the OpAmp
output stage with  = 4.
= 4.
![\begin{figure}
\begin{center}
\resizebox{11.4cm}{!}{
\psfrag{5_19Transfer_Av.crv...
...raphics[width=11.4cm,angle=0]{figures/5_19transfer.eps}}\end{center}\end{figure}](img500.gif) |
Figure 6.11:
Evolution of the node voltages during DC operating point calculation for the OpAmp
output stage with constant shunt conductance.
![\begin{figure}
\begin{center}
\resizebox{11.4cm}{!}{
\psfrag{5_19_noRs.crv:V1} {...
...degraphics[width=11.4cm,angle=0]{figures/5_19_noRs.eps}}\end{center}\end{figure}](img501.gif) |
The evolution of the node voltages during DC operating point calculation is
shown in Fig. 6.9. Best results were obtained with
 = 4. With ABC 34 iterations were needed and
KA = 34/30 = 1.13 whereas with DBC 38 iterations were needed and
KD = 38/31 = 1.226.
= 4. With ABC 34 iterations were needed and
KA = 34/30 = 1.13 whereas with DBC 38 iterations were needed and
KD = 38/31 = 1.226.
For the DC transfer characteristic the required number of iterations is shown
in Fig. 6.10. In addition
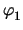 is shown to
represent the internal state of the circuit. In this case DBC is superior
compared to ABC.
is shown to
represent the internal state of the circuit. In this case DBC is superior
compared to ABC.
To demonstrate the importance of GSk the evolution of the node
voltages for a constant
GSk = 1/Gmin is shown in
Fig. 6.11. To obtain convergence at all, the global
damping parameter  had to be increased by a factor of 100 and 170
iterations were necessary.
had to be increased by a factor of 100 and 170
iterations were necessary.
Although ABC required less iterations than DBC this type of boundary
condition seems to have a negative impact on the condition of the system
matrix as each contact voltage depends on the node voltages of all other
contacts. Since an iterative solver is used which is very sensitive to the
condition of the matrix the total simulation time is unfortunately larger than
for DBC.




Next: 6.3.2 CML Inverter
Up: 6.3 Examples
Previous: 6.3 Examples
Tibor Grasser
1999-05-31
![\begin{figure}
\begin{center}
\resizebox{7.8cm}{!}{
\psfrag{Vin} {$\scriptstyle ...
...udegraphics[width=7.8cm,angle=0]{figures/gray_5_19.eps}}\end{center}\end{figure}](img498.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\begin{center}
\resizebox{11.4cm}{!}{
\psfrag{5_19_Av.crv:V1} {$\...
...udegraphics[width=11.4cm,angle=0]{figures/5_19conv.eps}}\end{center}\end{figure}](img499.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\begin{center}
\resizebox{11.4cm}{!}{
\psfrag{5_19Transfer_Av.crv...
...raphics[width=11.4cm,angle=0]{figures/5_19transfer.eps}}\end{center}\end{figure}](img500.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\begin{center}
\resizebox{11.4cm}{!}{
\psfrag{5_19_noRs.crv:V1} {...
...degraphics[width=11.4cm,angle=0]{figures/5_19_noRs.eps}}\end{center}\end{figure}](img501.gif)
![]() = 4. With ABC 34 iterations were needed and
KA = 34/30 = 1.13 whereas with DBC 38 iterations were needed and
KD = 38/31 = 1.226.
= 4. With ABC 34 iterations were needed and
KA = 34/30 = 1.13 whereas with DBC 38 iterations were needed and
KD = 38/31 = 1.226.
![]() is shown to
represent the internal state of the circuit. In this case DBC is superior
compared to ABC.
is shown to
represent the internal state of the circuit. In this case DBC is superior
compared to ABC.
![]() had to be increased by a factor of 100 and 170
iterations were necessary.
had to be increased by a factor of 100 and 170
iterations were necessary.