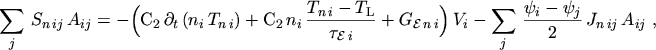The balance equations (2.184) to (2.186) are discretized
in the same manner as POISSON's equation. Integrating over the control volume
 and applying the theorem of GAUSS yields
and applying the theorem of GAUSS yields
The terms
 and
and
 are again discretized by
the box integration method. Writing the electric field as the negative gradient of the
electric potential and using the product rule the first term becomes
are again discretized by
the box integration method. Writing the electric field as the negative gradient of the
electric potential and using the product rule the first term becomes
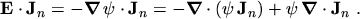 |
(3.26) |
Integration over the control volume
 , applying the theorem of
GAUSS, and approximating the integrals by sums yields
, applying the theorem of
GAUSS, and approximating the integrals by sums yields
where a linear variation of the potential between two grid points has been assumed. By
combining the sums the discrete representation of
 is obtained
is obtained
 |
(3.29) |
By analogy, the discretization of
 looks
looks
 |
(3.30) |
Using eqns. (3.29) and (3.30) the discretization of the continuity equations can be concluded
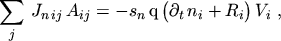 |
(3.31) |
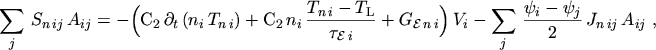 |
(3.32) |
 |
(3.33) |
where
 ,
,
 ,
,
 are the projections of the fluxes
are the projections of the fluxes
 ,
,
 ,
,
 onto the grid edge
onto the grid edge
 .
.
M. Gritsch: Numerical Modeling of Silicon-on-Insulator MOSFETs PDF






![]() and
and
![]() are again discretized by
the box integration method. Writing the electric field as the negative gradient of the
electric potential and using the product rule the first term becomes
are again discretized by
the box integration method. Writing the electric field as the negative gradient of the
electric potential and using the product rule the first term becomes