



Next: 4.5 Simulation of Polysilicon
Up: 4.4 Analysis of HBT
Previous: 4.4.2 Device Reliability
Subsections
The quality of Si N
N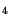 thin film passivation is of importance for the
reliability of III-V based HBTs. Both theoretical and experimental studies
have been conducted in order to minimize base leakage currents as a major
source of degradation. The effectiveness of the passivation of devices before
and after electrothermal stress aging is investigated by the means of
two-dimensional numerical simulations. For that purpose proper electrical and
thermal models are implemented in MINIMOS-NT allowing simulation of silicon nitride
as a wide bandgap semiconductor material.
thin film passivation is of importance for the
reliability of III-V based HBTs. Both theoretical and experimental studies
have been conducted in order to minimize base leakage currents as a major
source of degradation. The effectiveness of the passivation of devices before
and after electrothermal stress aging is investigated by the means of
two-dimensional numerical simulations. For that purpose proper electrical and
thermal models are implemented in MINIMOS-NT allowing simulation of silicon nitride
as a wide bandgap semiconductor material.
The non-ideal properties of the passivation are accounted by considering it as
a semiconductor material. A bandgap energy of 5 eV, relative dielectric
constant of 7, and constant carrier mobilities based on resistivity of

 -cm are used. Thus, previous results assuming an ideal
insulator material are verified. However, it has to be noted that the
transport properties in the insulator, being treated as a semiconductor,
strongly depend on the bandgap alignment on the insulator/semiconductor
interface which can be altered in the presence of surface charges.
-cm are used. Thus, previous results assuming an ideal
insulator material are verified. However, it has to be noted that the
transport properties in the insulator, being treated as a semiconductor,
strongly depend on the bandgap alignment on the insulator/semiconductor
interface which can be altered in the presence of surface charges.
The impact of the surface charge density is illustrated in Fig. 4.39
where simulation results for the electron current density at
V = 1.2 V without and with a surface charge density of
= 1.2 V without and with a surface charge density of
 cm
cm , respectively, are shown. Shockley-Read-Hall recombination
is taken into account also in the SiN with a trap density of
, respectively, are shown. Shockley-Read-Hall recombination
is taken into account also in the SiN with a trap density of
 cm
cm . Note, the decrease in the electron current density also in
the insulator in the presence of negative charges (Fig. 4.40).
. Note, the decrease in the electron current density also in
the insulator in the presence of negative charges (Fig. 4.40).
Figure 4.39:
Electron current density [A/cm ] at
V
] at
V =1.2 V: Simulation without surface charges
=1.2 V: Simulation without surface charges
|
|
Figure 4.40:
Electron current density [A/cm ] at
V
] at
V =1.2 V: Simulation with surface charge density of
=1.2 V: Simulation with surface charge density of  cm
cm
|
|




Next: 4.5 Simulation of Polysilicon
Up: 4.4 Analysis of HBT
Previous: 4.4.2 Device Reliability
Vassil Palankovski
2001-02-28
![]() = 1.2 V without and with a surface charge density of
= 1.2 V without and with a surface charge density of
![]() cm
cm![]() , respectively, are shown. Shockley-Read-Hall recombination
is taken into account also in the SiN with a trap density of
, respectively, are shown. Shockley-Read-Hall recombination
is taken into account also in the SiN with a trap density of
![]() cm
cm![]() . Note, the decrease in the electron current density also in
the insulator in the presence of negative charges (Fig. 4.40).
. Note, the decrease in the electron current density also in
the insulator in the presence of negative charges (Fig. 4.40).
![\resizebox{\halflength}{!}{
\includegraphics[width=\halflength]{figs/low2SiN.epsi}}](img795.gif)