



Next: 3.1.3 Device Delay
Up: 3.1 Delay Time
Previous: 3.1.1 Determining Delay Time
Interconnections contribute to the delay time two-fold: by
capacitive loading and by distributed-RC delay.
The interconnect capacitance
 adds to the capacitive load of the
driving stages. This effect dominates for short interconnections.
Interconnect capacitance
can be determined accurately with two and three-dimensional device
simulation [6,60].
For some purposes there are also analytical models [5,36],
which can also be calibrated to simulated or measured data.
The interconnect RC delay
adds to the capacitive load of the
driving stages. This effect dominates for short interconnections.
Interconnect capacitance
can be determined accurately with two and three-dimensional device
simulation [6,60].
For some purposes there are also analytical models [5,36],
which can also be calibrated to simulated or measured data.
The interconnect RC delay
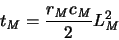 |
(3.4) |
dominates for long interconnections. Clearly, long interconnections will be
avoided by inserting repeaters to eliminate the square-law length dependence
and to regenerate the signal.
However, as the feature size is scaled down
 increases by
increases by
 and
and
 remains constant so that
the interconnect RC-delay does not scale with feature size.
This is a serious problem in deep-sub-micron technologies, where interconnect
delay starts to dominate [7,8,35].
remains constant so that
the interconnect RC-delay does not scale with feature size.
This is a serious problem in deep-sub-micron technologies, where interconnect
delay starts to dominate [7,8,35].
G. Schrom
![]() adds to the capacitive load of the
driving stages. This effect dominates for short interconnections.
Interconnect capacitance
can be determined accurately with two and three-dimensional device
simulation [6,60].
For some purposes there are also analytical models [5,36],
which can also be calibrated to simulated or measured data.
The interconnect RC delay
adds to the capacitive load of the
driving stages. This effect dominates for short interconnections.
Interconnect capacitance
can be determined accurately with two and three-dimensional device
simulation [6,60].
For some purposes there are also analytical models [5,36],
which can also be calibrated to simulated or measured data.
The interconnect RC delay