



Next: 3.1.4 Inverter Delay
Up: 3.1 Delay Time
Previous: 3.1.2 Interconnect Delay
A single transistor cannot be characterized like a complete digital circuit.
However, a transistor delay determined from key device data is strongly
related to gate delay and system speed.
The simplest expression for this is the so-called CV/I delay metric, where
a delay time is computed as
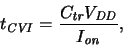 |
(3.5) |
where mostly
 (neglecting diffusion and miller
capacitance). (3.5) renders a delay time
which is in the order
of the actual circuit delay and shows a similar dependence on technology and operating
parameters. The CV/I metric is therefore very handy for simple trend analyses.
Apart from using analytical equations for
(neglecting diffusion and miller
capacitance). (3.5) renders a delay time
which is in the order
of the actual circuit delay and shows a similar dependence on technology and operating
parameters. The CV/I metric is therefore very handy for simple trend analyses.
Apart from using analytical equations for
 and
and
 these quantities can
be also measured or simulated directly. An accurate alternative method for
determining
these quantities can
be also measured or simulated directly. An accurate alternative method for
determining
 is given in Section 3.3.5.
Another way to account for device delay is to embed transistors in a
switch-level RC model, i.e., to compute an effective resistance
is given in Section 3.3.5.
Another way to account for device delay is to embed transistors in a
switch-level RC model, i.e., to compute an effective resistance
 so that
so that
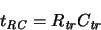 |
(3.6) |
For the CV/I metric the resistance would be
 .
.




Next: 3.1.4 Inverter Delay
Up: 3.1 Delay Time
Previous: 3.1.2 Interconnect Delay
G. Schrom