| Material |
 [g/cm [g/cm ] ] |
Reported Range |
References |
| Si |
2.33 |
2.238 - 2.239 |
[90,85,86] |
| Ge |
5.327 |
5.3234- 5.3267 |
[90,85] |
| GaAs |
5.32 |
5.307 - 5.36 |
[87,84,104] |
| AlAs |
3.76 |
3.76 |
[84,104] |
| InAs |
5.667 |
5.667 |
[88,84,73] |
| InP |
4.81 |
4.79-4.81 |
[96,84,73] |
| GaP |
4.138 |
4.13-4.14 |
[84,73] |
SiO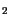 |
2.203 |
2.2 - 2.207 |
[85,86] |
Si N N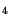 |
3.1 |
3.1 |
[85,86] |
|

