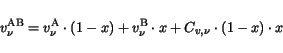Next: 3.6 Energy Relaxation Time
Up: 3. Physical Models
Previous: 3.4.5 High-Field Mobility for
The temperature dependence of the saturation velocities of electrons and holes in basic materials is calculated by
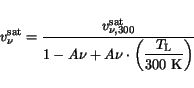 |
(3.134) |
The following model parameters from [182] are used.
Table 3.31:
Parameter values for velocity saturation model
| Material |
 [m/s] [m/s] |
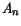 |
 [m/s] [m/s] |
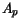 |
| Si |
1.0e5 |
0.26 |
0.704e5 |
0.63 |
| Ge |
0.7e5 |
0.55 |
0.63e5 |
0.61 |
| GaAs |
0.72e5 |
0.56 |
0.9e5 |
0.41 |
| AlAs |
0.85e5 |
0.55 |
0.8e5 |
0.3 |
| InAs |
0.9e5 |
0.57 |
0.5e5 |
0.3 |
| InP |
0.67e5 |
0.68 |
0.5e5 |
0.3 |
| GaP |
0.88e5 |
0.30 |
0.5e5 |
0.3 |
|
In the case of alloy materials the temperature dependent saturation velocities are
calculated first using (3.134). For an alloy
 the model suggests a quadratic interpolation between the
saturation velocities for electrons of the basic materials (A and B) depending on the
material composition
the model suggests a quadratic interpolation between the
saturation velocities for electrons of the basic materials (A and B) depending on the
material composition  . In case of holes a linear interpolation is assumed.
. In case of holes a linear interpolation is assumed.
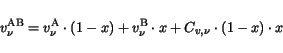 |
(3.135) |
The bowing parameters  and
and  are summarized in the following table.
are summarized in the following table.
Table 3.32:
Parameter values for velocity saturation model for alloy materials
| Material |
 [m/s] [m/s] |
 [m/s] [m/s] |
| SiGe |
-2.28e5 |
0.0 |
| AlGaAs |
-0.0512e5 |
0.0 |
| InGaAs |
-0.196e5 |
0.0 |
| InAlAs |
-2.13e5 |
0.0 |
| InAsP |
0.0 |
0.0 |
| GaAsP |
0.0 |
0.0 |
| InGaP |
-0.3e5 |
0.0 |
|




Next: 3.6 Energy Relaxation Time
Up: 3. Physical Models
Previous: 3.4.5 High-Field Mobility for
Vassil Palankovski
2001-02-28
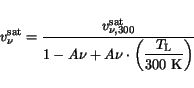
![]() the model suggests a quadratic interpolation between the
saturation velocities for electrons of the basic materials (A and B) depending on the
material composition
the model suggests a quadratic interpolation between the
saturation velocities for electrons of the basic materials (A and B) depending on the
material composition ![]() . In case of holes a linear interpolation is assumed.
. In case of holes a linear interpolation is assumed.