



Next: 4.2.2 Simulation Results
Up: 4.2 High Power GaAs
Previous: 4.2 High Power GaAs
All four HBT structures are MOCVD epitaxially grown on GaAs substrates. The first
device, later on referred to as Dev. 1, has the following layer sequence: The
cap is formed by an n -InGaAs/n-GaAs layer. The emitter consists of 80 nm
Si-doped n-Al
-InGaAs/n-GaAs layer. The emitter consists of 80 nm
Si-doped n-Al Ga
Ga As with 20 nm graded layers on its top and
bottom, respectively. The 120 nm GaAs base is carbon doped (p
As with 20 nm graded layers on its top and
bottom, respectively. The 120 nm GaAs base is carbon doped (p = 3.10
= 3.10 cm
cm ), followed by a 700 nm GaAs collector (n
), followed by a 700 nm GaAs collector (n = 2.10
= 2.10 cm
cm )
and a 700 nm GaAs subcollector (n
)
and a 700 nm GaAs subcollector (n = 5.10
= 5.10 cm
cm ). The simulated
device structure is shown in Fig. 4.13.
). The simulated
device structure is shown in Fig. 4.13.
Figure 4.13:
Simulated device structure of AlGaAs/GaAs HBT
|
|
In two devices (Dev. 2 and Dev. 3) the graded AlGaAs layer next to the
base-to-emitter junction is replaced by a 20 nm InGaP ledge layer (n =
4.10 cm
cm and 3.10
and 3.10 cm
cm , respectively). Both devices
differ in base carbon doping (p
, respectively). Both devices
differ in base carbon doping (p = 3.10
= 3.10 cm
cm vs. 4.10
vs. 4.10 cm
cm ) and layer thickness (80 nm vs. 120 nm). A 40 nm InGaP emitter (n =
4.10
) and layer thickness (80 nm vs. 120 nm). A 40 nm InGaP emitter (n =
4.10 cm
cm ) HBT with 120 nm base thickness is the last considered
device type (Dev. 4). All HBTs are processed by etching a double mesa
structure and passivated by Si
) HBT with 120 nm base thickness is the last considered
device type (Dev. 4). All HBTs are processed by etching a double mesa
structure and passivated by Si N
N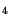 . The simulated device structure is
shown in Fig. 4.14.
. The simulated device structure is
shown in Fig. 4.14.
Figure 4.14:
Simulated device structure of InGaP/GaAs HBT
|
|




Next: 4.2.2 Simulation Results
Up: 4.2 High Power GaAs
Previous: 4.2 High Power GaAs
Vassil Palankovski
2001-02-28
![\resizebox{1.2\halflength}{!}{
\includegraphics[width=1.2\halflength]{figs/alhbt.eps}}](img752.gif)
![]() cm
cm![]() and 3.10
and 3.10![]() cm
cm![]() , respectively). Both devices
differ in base carbon doping (p
, respectively). Both devices
differ in base carbon doping (p![]() = 3.10
= 3.10![]() cm
cm![]() vs. 4.10
vs. 4.10![]() cm
cm![]() ) and layer thickness (80 nm vs. 120 nm). A 40 nm InGaP emitter (n =
4.10
) and layer thickness (80 nm vs. 120 nm). A 40 nm InGaP emitter (n =
4.10![]() cm
cm![]() ) HBT with 120 nm base thickness is the last considered
device type (Dev. 4). All HBTs are processed by etching a double mesa
structure and passivated by Si
) HBT with 120 nm base thickness is the last considered
device type (Dev. 4). All HBTs are processed by etching a double mesa
structure and passivated by Si![]() N
N![]() . The simulated device structure is
shown in Fig. 4.14.
. The simulated device structure is
shown in Fig. 4.14.